Introduction
Having finished the 750+ page tome to Capital by Thomas Piketty well over a year ago, I have just gotten around to writing up what I learned. In attempting to summarize this book, I realize that there is no way I can cover everything I learned. Quite simply, Piketty has blown my mind with the depths of his research. This book is the deepest source I have ever read on how capital behaves and why wealth and income inequality are two sides of different coins.
I figure that the best approach with this write-up is to break it down into manageable chunks. What follows below is a summary of the theoretical characteristics of Capital and how it behaves in the world today as well as in the past. I’ll unpack the features of income, capital, and output and how each of these dynamics interplay with one another.
The next write-up at a later date yet to be determined, will delve into the impacts that Capital has had on inequality. I’ll unpack the structure of inequality and some potential solutions that Piketty mentions. This review is by no means a political or opinion piece. I am simply sharing some of the learnings I received from diving into this book.
With that, let’s dive in…
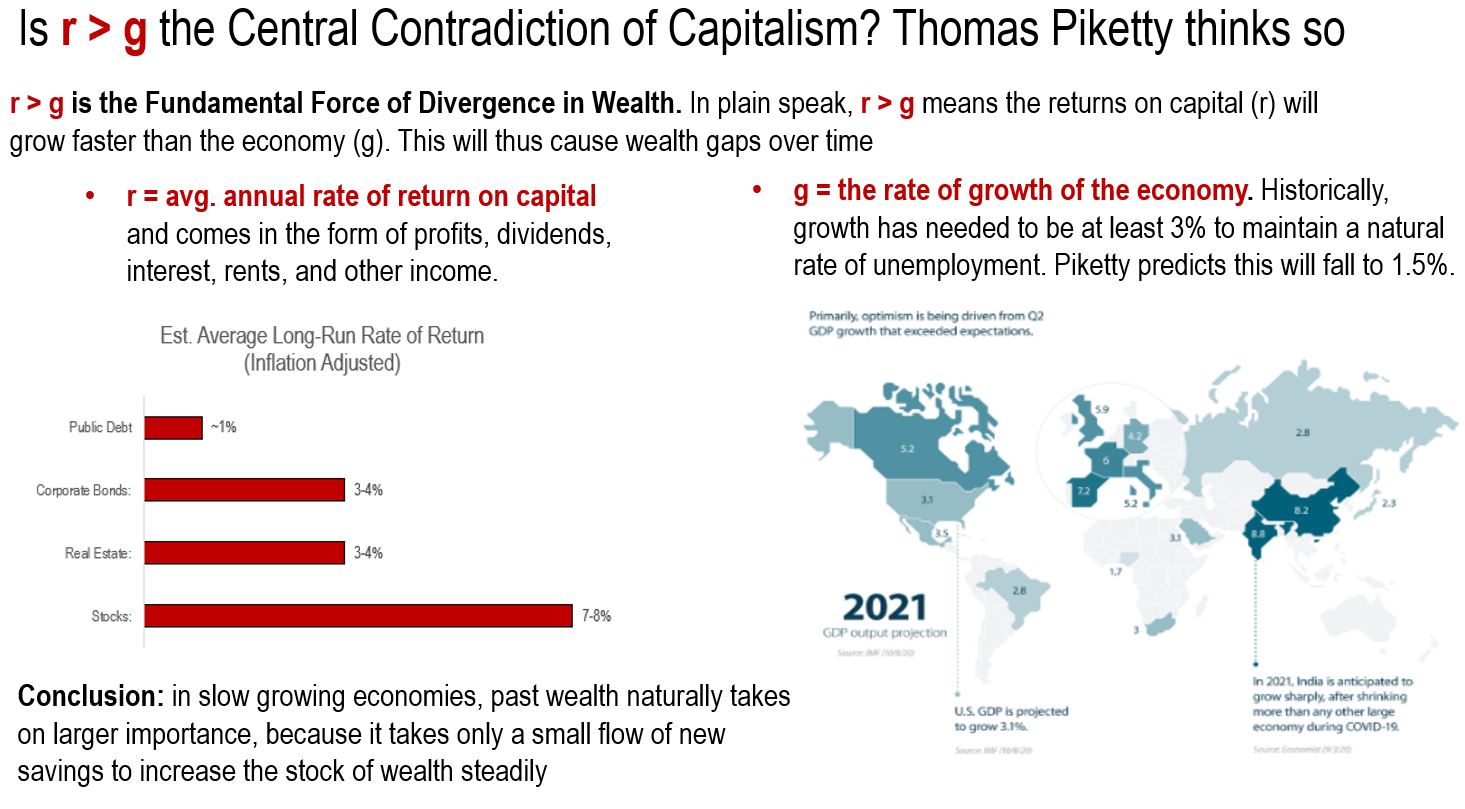
Is r > g the Central Contradiction of Capitalism?
The first concept that Piketty spends time unpacking is the relationship between returns on capital and the overall growth rate of the economy. Piketty boldly states that growth in the future will slow and capital will be that much more important. As economic growth slows and falls below the average rate of return on capital, past wealth naturally takes on a larger importance. This is simply because it takes only a small flow of new savings to increase the stock of wealth steadily.
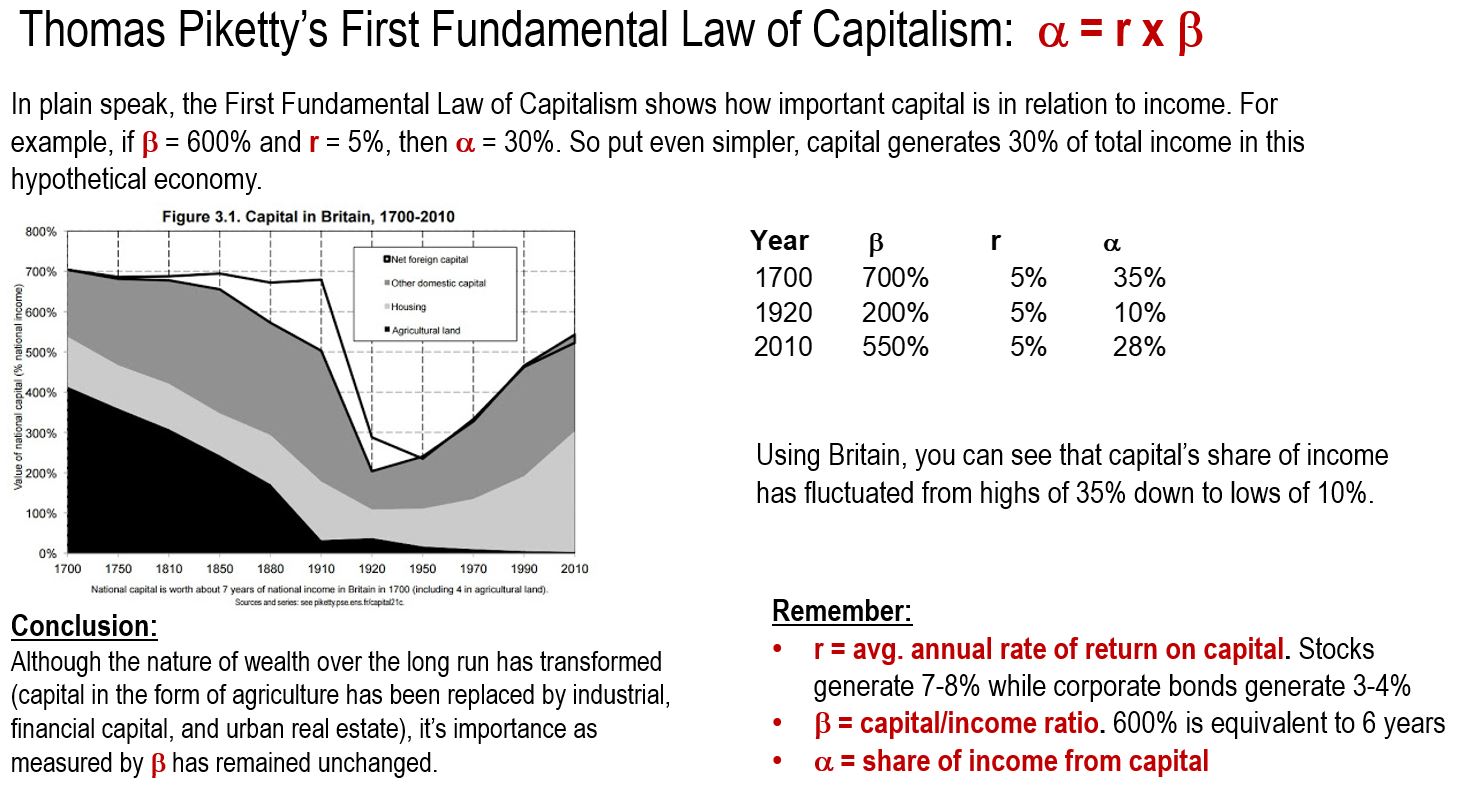
Thomas Piketty’s First Fundamental Law of Capitalism
The second concept that Piketty spends time unpacking is what he calls his First Fundamental Law of Capitalism. This law shows how important capital is in relation to the national income of a country. As the nature of wealth over the long run continues to transform (i.e., capital used to be agricultural and has since been replaced by industrial, financial capital, and urban real estate), its importance as measured by the capital/income ratio has remained steady and unchanged.
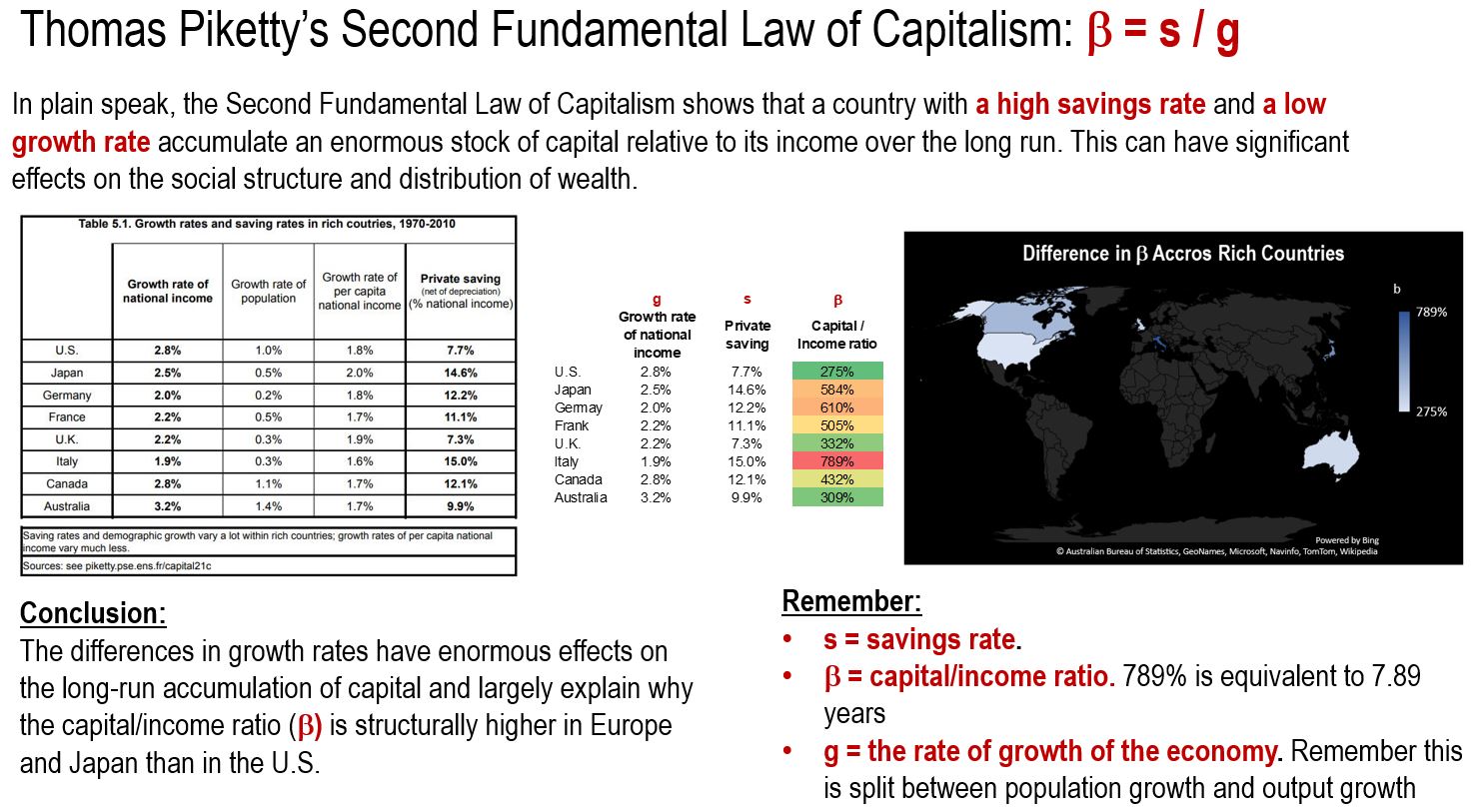
Thomas Piketty’s Second Fundamental Law of Capitalism
The third concept that Piketty spends time unpacking is what he calls his Second Fundamental Law of Capitalism. This law shows that countries with high savings rates and low growth rates accumulate enormous stocks of capital relative to their incomes over the long run. This can have significant effects on the social structure and distribution of wealth in a country. Piketty emphasizes that the impacts of this law are gradual and take decades to manifest. Boldly, Piketty predicts that by 2100 the entire planet could look like Europe at the turn of the 20th century with a capital/income ratio of 6-7 years.
The Dynamics of the Capital/Income Ratio in Europe and the U.S.
By investigating the dynamics of the capital/income ratio of Britain, France, Germany, and the United States, Piketty uncovers that the nature of capital in these rich countries has changed: capital was once mainly land but has now primarily become housing, industrial, and financial assets. But capital’s importance remains the same.
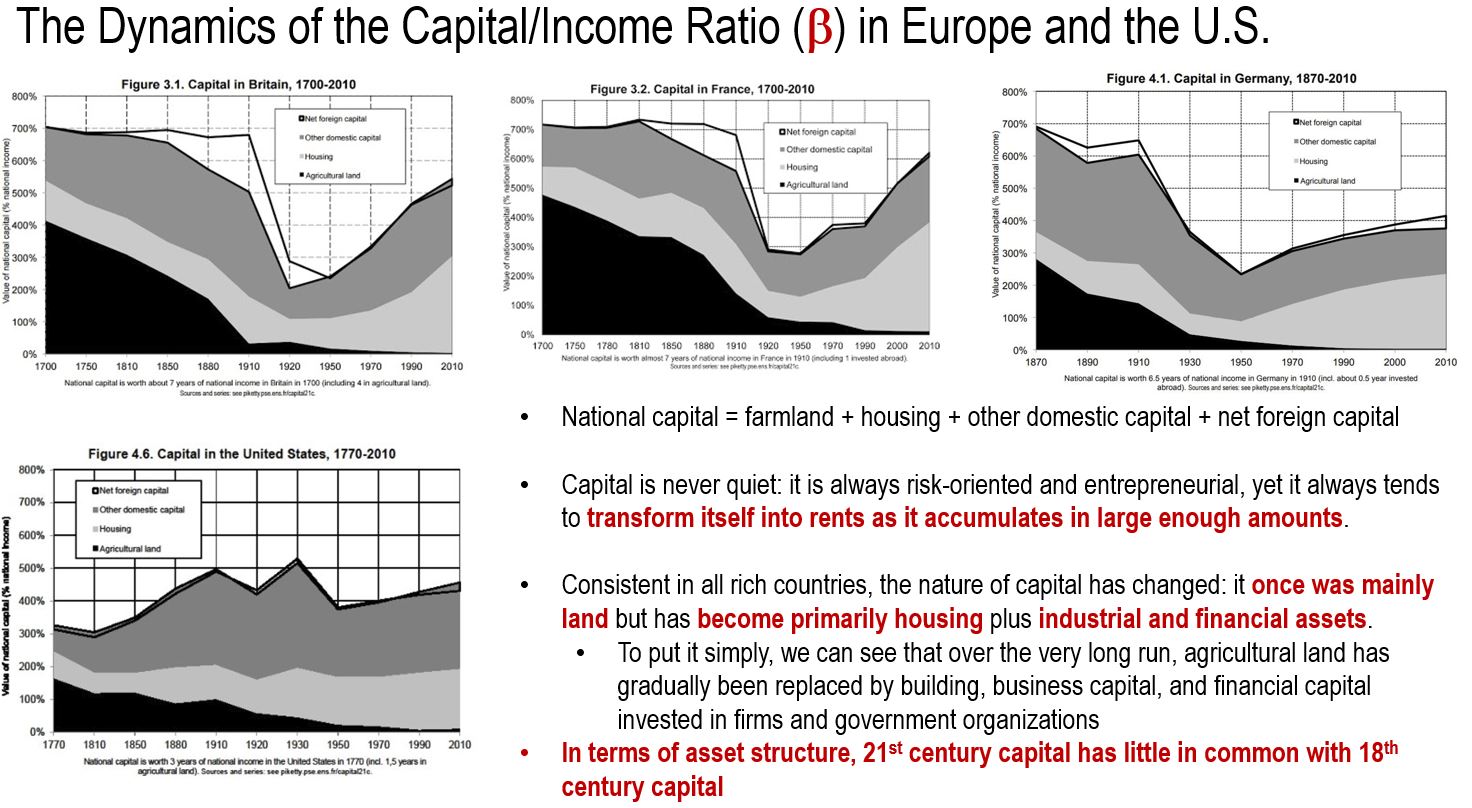
The Dynamics of the Capital/Income Ratio in Britain
In Britain, private wealth in 2010 accounted for 99% of national wealth and the bulk of the pubic debt in practice was owned by a minority of the population. Britain in summary is a country with accumulated capital based on public debt and the reinforcement of private capital.

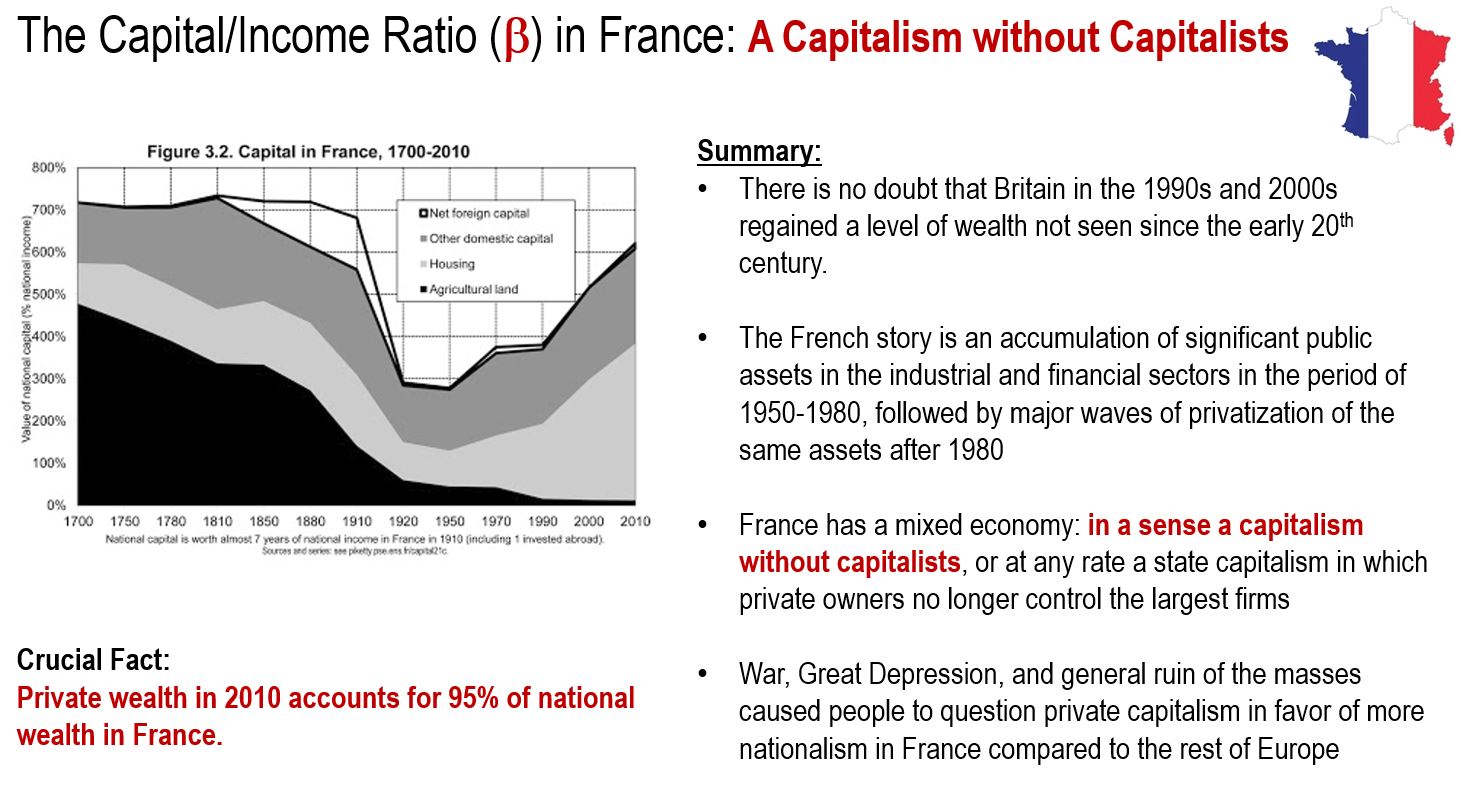
The Dynamics of the Capital/Income Ratio in France
In France, private wealth in 2010 accounted for 95% of national wealth and the bulk of wealth in France was driven by accumulations of significant public assets in the industrial and financial sectors followed by major waves of privatization of these same assets. In a sense, France is a country with a model of Capitalism without Capitalists.
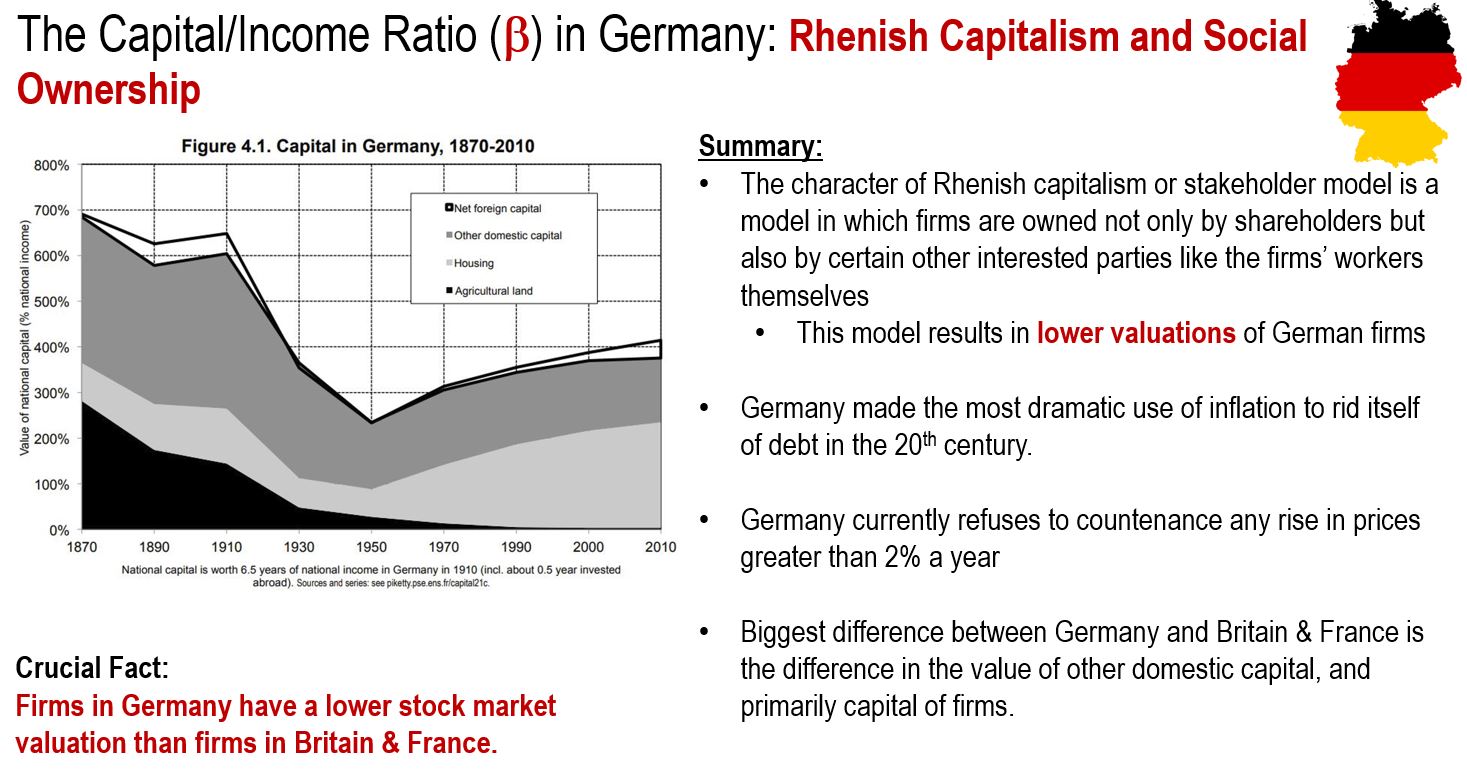
The Dynamics of the Capital/Income Ratio in Germany
In Germany, capitalism takes on a more social ownership point of view. Prevalent in the German marketplace is the stakeholder model of business where firms are owned not only by shareholders but also by certain other interested parties like the firms’ workers themselves. This Rhenish Capitalism has resulted in lower stock market valuations for German firms when compared to British & French firms.
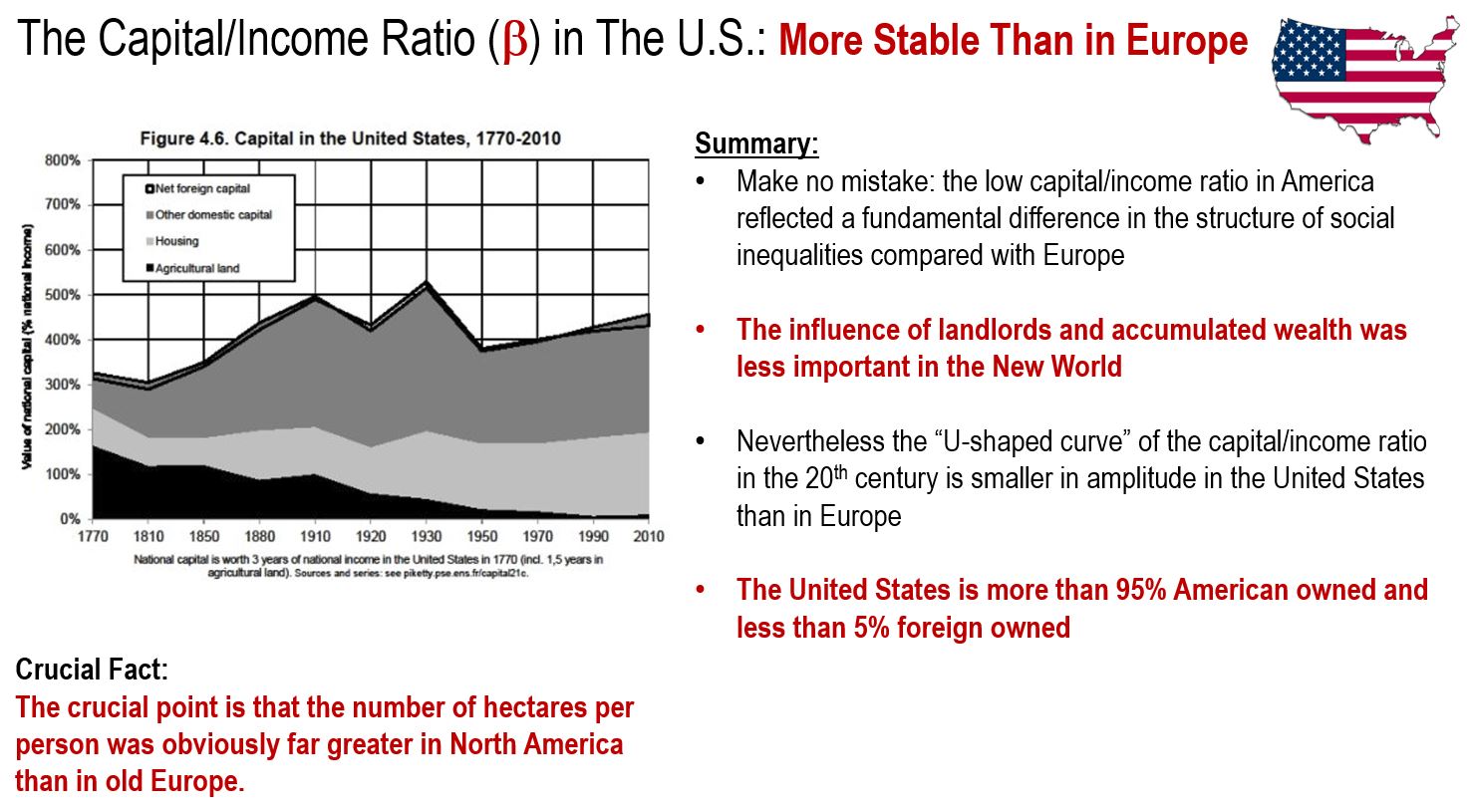
The Dynamics of the Capital/Income Ratio in the United States
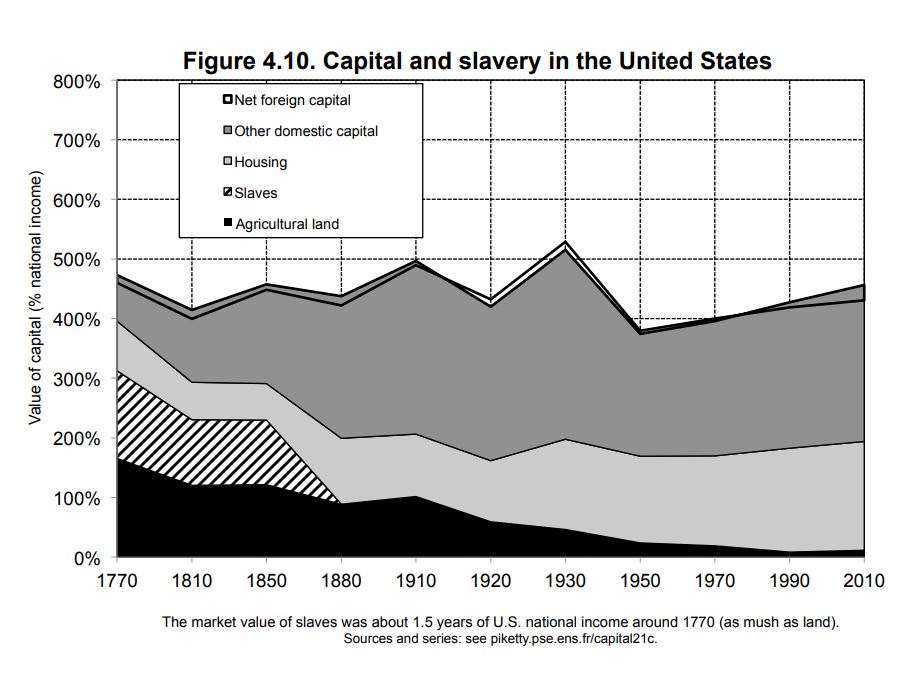
In the United States, more than 95% of the assets are American-owned but the influence of landlords and historically accumulated wealth was less important in the U.S. than in Europe. However, the structure of capital in the United States took on a different form. Specifically in the South, slave capital largely supplanted and surpassed landed capital. So much so, that the total market value of slaves represented nearly a year and a half of U.S. national income in the late 18th and first half of the 19th century.
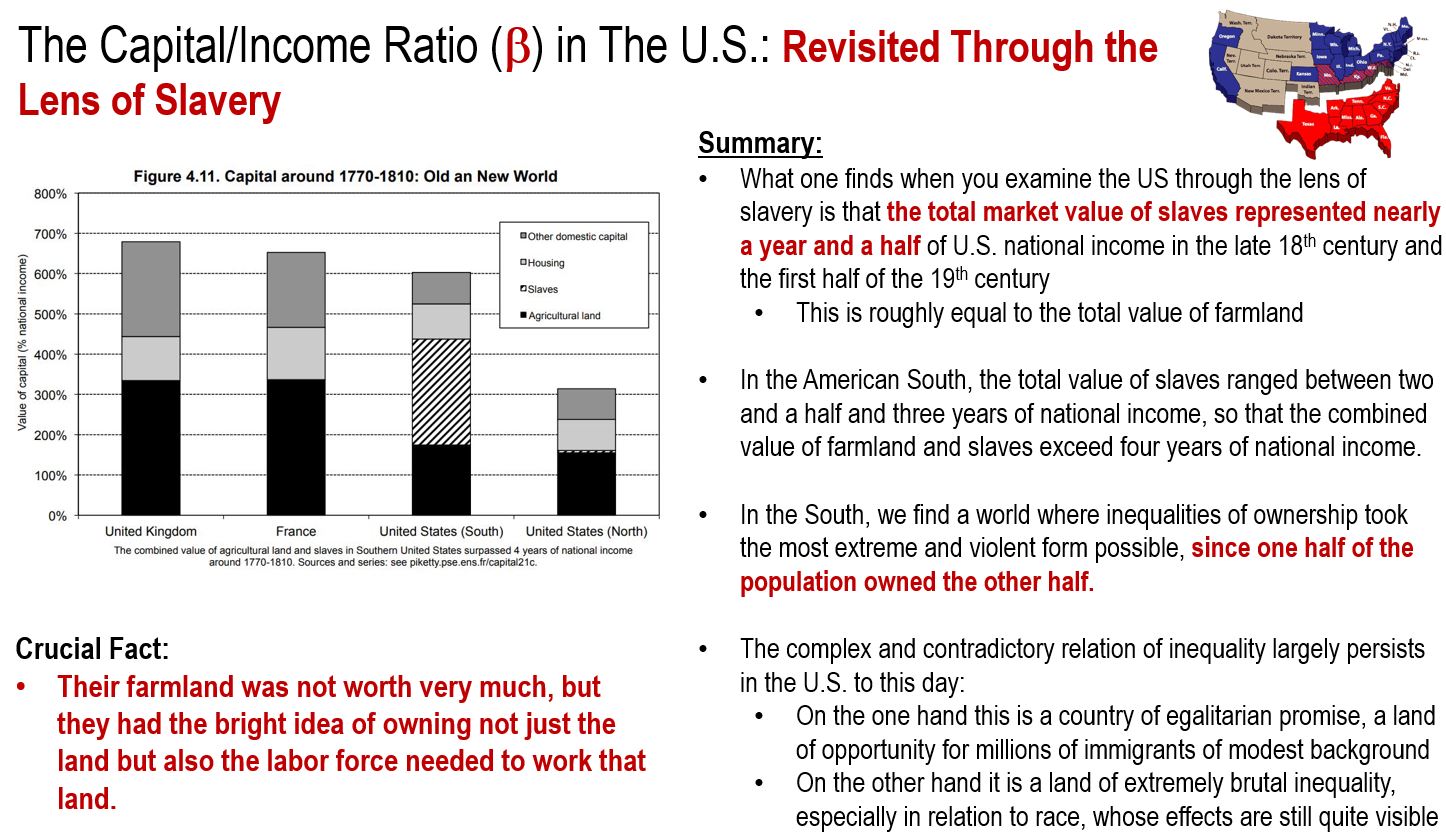
Conclusion
A market economy based on private property, if left to itself, contains power forces of divergence, which are potentially threatening to democratic societies and to the values of social justice on which they are based. My next write-up on Capital in the Twenty-First Century by Thomas Piketty will dive into the immense inequalities of wealth that have occurred as a result of the natural dynamics of capital.
Downloadable Content
Extras
Brian Nwokedi’s Book Review on Goodreads
Brian Nwokedi’s Twitter Thread on Capital and Thread on the Structure of Inequality
Brian Nwokedi’s Booknotes on Youtube and The Structure of Inequality
Author’s Twitter: @PikettyLeMonde
Author’s Website: Thomas Piketty
Video: New thoughts on capital in the twenty-first century
Netflix Documentary Here